Industry 4.0 - Guide to Fourth Industrial Revolution
The Fourth Industrial Revolution or Industry 4.0, is the ongoing transformation of traditional manufacturing and industrial practices combined with the latest smart technology. This primarily focuses on the use of a large-scale machine to machine communication (M2M) and Internet of Things (IoT) deployments to provide increased automation, improved communication, and self-monitoring, as well as smart machines that can analyze and diagnose issues without the need for human intervention.
What is meant by Industry 4.0?
Industry 4.0 is signaling a change in the traditional manufacturing landscape. Also known as the Fourth Industrial Revolution, Industry 4.0 encompasses three technological trends driving this transformation- connectivity, intelligence, and flexible automation.
Industry 4.0 describes the growing trend towards automation and data exchange in technology and processes within the manufacturing industry, including- The Internet of Things (IoT), The Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT), Cyber-physical Systems (CPS), Smart Manufacturing, Smart Factories, Cloud Computing, Additive Manufacturing, Big Data, Robotics, Cognitive Computing, Artificial Intelligence & Blockchain, etc.
This automation creates a manufacturing system whereby the machines in factories are augmented with wireless connectivity and sensors to monitor and visualize an entire production process and make autonomous decisions.
What is the evolution of the Industrial Revolution?
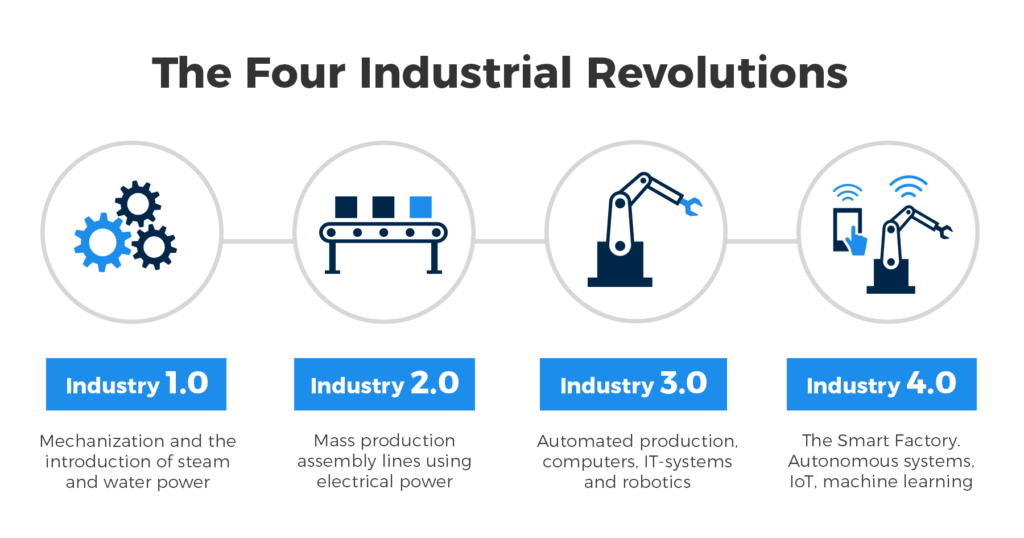
- The first industrial revolution came with the advent of mechanization, steam power, and water power.
- The second industrial evolution revolved around mass production and assembly lines using electricity.
- The third industrial revolution came with electronic and IT systems and automation.
- The fourth industrial revolution is associated with cyber-physical systems.
Impact of Industry 4.0 post COVID-19?
- Industry 4.0 is not only as relevant as it was before the global COVID-19 emergency; it is actually far more relevant moving forward.
- COVID-19 is causing radical shifts in workflow across the globe as millions practice social distancing and comply with self-quarantine recommendations.
- The pandemic's dramatic appearance has accelerated numerous trends while slowing others.
- Although businesses have had reason to embrace digital workflows in the past, COVID-19 has provided another strong incentive to move towards a smart factory, complete with smart manufacturing or smart printing processes.
- While conventional wisdom says that dedicated office space is required to maximize productivity but this theory is being put to the ultimate test during COVID-19.
- The integration of digital infrastructure to streamline public health to respond to the COVID-19 pandemic is very crucial in the context of epidemic forecasting and decision-making, one such example in India is the Aarogya Setu app by Government of India.
- The fastest scalable solution to India's COVID-19 challenge was to employ digital technology for diagnosis and for contact tracing. Aarogya Setu app can also be tapped for providing telemedicine, especially in remote parts, during this moment of crisis.
- This digital infrastructure implementation increasingly fuels the digital transformation initiatives within an organization as well. In the present situation, we are seeing major occurrences worldwide, including soaring adoption of online services, an enormous requirement for internet services, and enhanced connectivity among industries, regardless of their sizes.
- The impact of the COVID-19 pandemic has demonstrated the value of IT and digital transformation across industries and businesses and they must utilize this time to speed up the transition.
- It has been demonstrated in the enhanced corporate ability of long-distance collaborative work, wide recognition of the value of digital transformation and information technology among all employees, and the ability to market online and business development.
- Going forward, many organizations may adopt remote working agreements as strategies to reduce costs, improve productivity, and increase worker satisfaction.
- Many manufacturers are increasing efforts to equip their human workers with digital connected-worker tools that incorporate safety checks into workflows, ensure collaboration with colleagues when physical contact is off the cards and other such processes that ultimately balance business continuity and employee health.
- Manufacturers who understand and act on this new normal will have ample opportunities for growth in this era of Industry 4.0.